Tver
Deutsch Russian
Russian
Table of Contens
Tver: brief historical information
Between
two capitals (geographical location of the city)
Hospital
home (a few words about Tver culture)
Everything about the
town of Tver
Survey
of social-aconomic development of Tver in 1995
Tver: brief historical information
Tver is truly called one of the oldest Russian towns. It's rather difficult
to determine the precise date of birth. It is only known that already at
the beginning of the Xll-th century in the mouth of the Tvertza river there
appeared a fortress, which was to be the prototype of Tver. The first direct
record of our town in chronicles is referred to 1209. In 1246 Tver became
the capital of Tver princedom.
Our town differs from the other ones by two features: skill of its
towns-men and aspiration for sovereignty. And if skill of Tver curriers,
foundry workers, jewellers brought fame to the town, then struggle for
independence often plunged Tver, into many severe trials. For long decades
of years Tver rivalled in Moscow for the right to be the town-consolidator,
the town-elder brother. In 1305 Michail Yaroslavich Tverskoy calls himself
not only grand duke of Vladimir but all the Russia. The death of Michail
Tverskoy in the Horde (he fell a pray to the intrigue of Yuriy, Moscow
duke) deprived the town of the head. None of Tver dukes after Michail 's
death could resist Moscow dukes. In 1485 Tver princedom was subjected to
Moscow. But the XV-th century will remain in the memory of the inhabitants
of Tver not only by this event. In 1468-1474 Tver merchant Afanasiy Nikitin
went for a trip to India. His book " Sailing over three seas" still remains
a monument of history, culture and art.
The Middle Ages of Russia were marked by rapid growth of workmanship.
Mikula Krechetnikov, the gunsmith, became famous all over the Russia. Tver
builders, jewellers, engravers were also famous. But let's be carried away
for some centuries further ahead to the second half of the XVIII century.
The fire in 1763 considerably devastated wooden and remote Tver. And it
was planned and built up over again by Decree of Ekaterina the Second.
Outstanding architectors P.Nikitin, A.Kvasov, S.Obukhov, M.Kazakov were
engaged in this matter. Present planning of the central part of Tver is
the result of their creative work.
Tver went through the period of violent growth at the end of the last
century. Manufactures, factories and plants were built. At that time the
waggon-building plant was built by a french-belgium company, which is still
the object of pride of the inhabitants of Tver. There were always many
churches in Tver. In the last years some efforts were made to revive the
look of the old Tver, to keep uniformity in style.
There is no doubt Tver may have a beautiful future. We have everything
for it. The only thing to do is to work properly.
Between
two capitals (geographical location of the city)
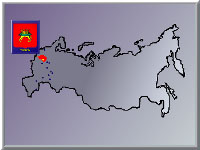 The location of Tver is an object
of many years' discussions. On the one hand one cannot but admit tat the
place of the city between Moscow and St.Petersburg is extremely economically
profitable. Tver automatically became a large transport junction, crossing
of many tourists routes and, tours. On the other hand closeness to the
capitals creates considerable complications, since both of these megalopolis'
draw human, financial and economic potential of Tver.
The location of Tver is an object
of many years' discussions. On the one hand one cannot but admit tat the
place of the city between Moscow and St.Petersburg is extremely economically
profitable. Tver automatically became a large transport junction, crossing
of many tourists routes and, tours. On the other hand closeness to the
capitals creates considerable complications, since both of these megalopolis'
draw human, financial and economic potential of Tver.
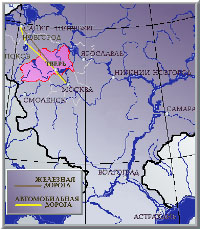 Our
city occupies the territory more than 146 square kilometres. It is 167
km far from Moscow and 485 km far from St.Petersburg. It is located at
the confluence of the rivers Volga, Tvertza and Tmaka. It is connected
with Moscow by three transport main lines: railways, highways and waterways.
In Migalovo region there is one of the largest military aerodromes. For
some years the plans on its widening and turning into a large transport
aerodrome are being worked out. If it takes place Tver will be one of the
biggest transport airport in Russia.
Our
city occupies the territory more than 146 square kilometres. It is 167
km far from Moscow and 485 km far from St.Petersburg. It is located at
the confluence of the rivers Volga, Tvertza and Tmaka. It is connected
with Moscow by three transport main lines: railways, highways and waterways.
In Migalovo region there is one of the largest military aerodromes. For
some years the plans on its widening and turning into a large transport
aerodrome are being worked out. If it takes place Tver will be one of the
biggest transport airport in Russia.
Favourite geographical location led to high concentration of wholesale
distributors in the region and in the city. Tver has favourable preconditions
for deriving benefit from its location on trade-political landscape of
Europe.
Hospital home
(a few words about Tver culture)
The century-old history of Tver is closely connected with its culture.
The literary works of the 11-16 centuries reflect the town life full of
events and anxieties. In the 12-th century Tver principality became the
centre of opposition to the Golden Horde Tatar mongolian yoke. In 1327
there was a popular uprising against Tatar yoke. This event was described
in the famous old-Russian work "The Story of Shelkan". "The story of Michail
Yaroslavich Tverskoy", chronicle created by Father Superior Alexander is
a call to Russian people for fight and liberation of Russia. In the beginning
of the 14-th century Tver Duke Michail began to struggle for the leading
role with Moscow dukes and he became the victim of this struggle. According
to the denunciation of Moscow duke he was prosecuted in betrayal of the
Golden Horde and in 1318 he was executed. The struggle for the right to
be at the head of the movement for liberation between dukes of Moscow and
Tver finished with the victory of Moscow. Since then Tver has become a
province, and Tver Otroch monastery became a prison for political opposition
of Moscow duke.
In the XVI-th century Metropolitan Philip the head of Russian Church
and Maxim Grek, a theological writer, remained in a dungeon of the Otroch
monastery for many years. His famous books were written here.
But it is all a remote past. The closer our days the more famous people
of culture we meet. Tver was always famous for its hospitality. Krylov
spent his childhood in Tver. Dostoevsky on his return from Siberian penal
servitude was living here for two months. Persecuted Mandelshtam was also
here. Near for two years the Great Saltykov-Schedrin was the vice-governor
of Tver. It was counted up by specialists that Pushkin passed through Tver
for thirty times. Radischev and Lermontov, Gogol and Turgenev, Ostrovsky
and Tolstoy were also here in the course of their journey. Karamzin and
Venetsianov, Mayakovsky, Akhmatova, Gumilev also visited Tver.
Nowadays there are three theatres: drama, puppet and the young spectator
theatre. After capital repairs Philarmohnic Society has become the favourite
place of meeting of music lovers. Tver is one of the few cities having
its own organ. A remarkable collection of Russian and Old Russian works
of art is submitted in the Picture Gallery. Collections of the Tver United
Historical and Architectural and Literary museum strike of its wealth.
Museums of Tver mode of life, of Saltykov-Schedrin, of Serov are its branches.
Several generations of remarkable painters were grown for twenty years
in Art School by Venetcianov. Their works are regularly exhibited in show
rooms of the Art Gallery, the Union of painters of Russia.
Music and music-pedagogical colleges favour the music life of the city.
In spite of the crisis of cinematographic industry all over the country
there are movie-houses "Zvezda" and "Vulkan" which are very popular among
the citizens.
Public organisations exert influence upon the cultural life of the
city: Music Society arranges remarkable concerts and festivals. The Union
of painters of Russia regularly organizes exhibitions, the club of students
of local lore, club of amateur photographers.
There are more then dozens of libraries in the town. The main libraries
are the Gorky public library, the Hertzen public library and the Pushkin
children's library.
Tver is the city of students. Young people all over Russia come to
Tver to get knowledge. There is the Tver State University, Technical University,
State Medical Academy, Agricultural Academy in our town. The cultural life
has a great influence on economics. Educated and cultured people always
welcome everything new and are ready to use new technique.
That's why the culture of Tver is not only its past but its future
to a great extend.
Everything about the town
of Tver
Tver is one of the biggest administrative industrial and cultural centres
of Russia. It is a district centre. The population of the town is about
459 thousand people, its territory is more than 146 square kilometres.
About 200 thousand people are involved in national economy, and 70% of
them work in material production, 20% - in social and cultural sphere and
science, 10% - in municipal economy, administration, credit and insurance
institutions. The main number of the working people are involved in industry.
Near 80 large enterprises produce almost 35% of industrial production of
the district. Tver is All-Russian leader of the production of carriages
and excavators. Tver takes a remarkable place in printing and textile,
in production of artificial material and synthetic fibres.
The leading branches of the municipal industries are light and textile,
engineering and metal working which accordingly account 25% and 36% in
value terms from the total output.
A large part (up to 12%) is presented by food processing and power
energetic industries. Parts of chemical and printing industries are equal
7% and 2,6% correspondingly. Enterprises of building, wood manufacture
and glass industries consist about 6%.
Energy needs of the city are provided with three thermoelectric power
stations, which are under authority of the joint-stock company "Tverenergo"
and 28 boiler-rooms.
Tver is supplied with three gas-mains: Serpukhov - St.Petersburg, Ukhta
- Torzhok (" Severnoye Siyanie ") and Belousovo - St.Petersburg. The city
is supplied with four kinds of urban transport: trams, buses, trolleybuses
and taxis, with the exception of the private joint-stock company "Tverskoye
taxi". It is a municipal enterprise. Their portions in people's transportation
are follows: by bus - about 30%, trolleybus - 70%, taxi - less than 1%.
There are four educational institutions in the city. More than four thousand
specialists take university degree every year. Near seven thousand students
at eleven specialised secondary institutions learn the following professions:
chemical industry workers, mechanic operators, builders, textile workers,
teachers, accounting and banking, cultural and education work, etc.
Scientific and research potential of the town is presented by 40 scientific
institutions and planning organisations of different kind.
A wide net of public health institutions include 24 hospitals, maternity
hospitals and health with the total number of about thousand units and
46 out-patient clinics.
Telephone network provides Russian and international communication
channels. The telephone station capacity is about 70 thousand numbers.
Joint-stock company "Tver Cellular Communications" is registered and it
has already started working . Buying of the full block of bonds [27 pieces
having nominal cost of 100000 roubles), gives the right to install a telephone
out of order. The Joint-stock company "Electrosvyaz", bank "Finkor-Credit"
and trust corporation "Zolotoy dozhd" carry on the loan.
More than 70% of more than 7 thousand business being registered are
of new form of ownership: Joint-stock companies, partnership, private business,
etc.
Participating in Federal programme of business support promotes private
business.
Tver develops its external economic links. Close relations are established
with the following cities: Khaymmenlinne (Finland), Osnabruek (Germany!,
Inkou (China!, Buffallo (USA) Bezanson [France!, Kaposhvar (Hungary).
Tver takes part in housing and information projects of World Bank of
Reconstruction and Development. In the town is being searched the different
ways of solving the housing problems: subsidisation, loans, certificates
including.
Survey of
social-aconomic development of Tver in 1995
In the first half-year of 1995 there appeared indications of relative economic
stabilisation in the town, though there are the factors putting obstacles
in constant rise of economic activity and real private incomes.. Volume
of output was 950 million roubles for this period, and it declined at 14%
as against 28% at the same period of the last year. Pace of falling was
slackened every month, and in June a small increase of 0,7% was achieved.
Decline in consumer goods output is 26% to the level of 1994, 44% as
for the light industry goods. Fall of production of cotton fabric, knitted
wear made up 60-70% and confectionery - 50%. Rates of investments recession
are considerably shortened. [first half-year of 1994 to first half-year
of 1993 is 51 %, 1995 to 1994 - 4%).
There is considerable slackening of investments to the industrial construction.
Nowadays 18 objects of production are under construction. As for the volumes
of housing construction it has greatly risen. 104,4 thousand square metres
of dwelling were put into commission at the expense of all sources of financing
[14% more in comparison with the corresponding period of the last year).
At the same time finance condition of enterprises is still unstable.
Growth of income is of inflation nature and it is greatly behind the price
growth (in industry for the period January - June more than twice).
Mutual non-payments, overdue especially, had a negative influence over
economic impact in the town.
In spite of the slackening of the rate of inflation growth, consumer
prices have risen in 1,8 times for a half year.
More over the increase of prices was higher than the salary growth,
and it couldn't have influenced the cost of living. In the result, according
to the data of social investigation 80% of citizens appreciated their financial
position as "exclusively hard" and "difficult". The fall of consuming capacity
of the population lead to the reduction of turnover and public services
in comparison with the level of the last year as 9% and 22% correspondingly.
As for the city market state there exist slackening of process of displaces
workers in stuff reduction and a small rise o unemployment rate.
As of July 1, 1995 it is 1,4% from the quantity of economically active
population (2863 men).
80% unemployment people, are women, 35% - young people. The highest
number of unemployment workers (58%) are high and special educated people.
Demographic situation is characterised by stabilisation of natural
movement of population and conservation of tendency of remarkable growth
of number of new-comers.
To the Table of contence To
Homepage
 The location of Tver is an object
of many years' discussions. On the one hand one cannot but admit tat the
place of the city between Moscow and St.Petersburg is extremely economically
profitable. Tver automatically became a large transport junction, crossing
of many tourists routes and, tours. On the other hand closeness to the
capitals creates considerable complications, since both of these megalopolis'
draw human, financial and economic potential of Tver.
The location of Tver is an object
of many years' discussions. On the one hand one cannot but admit tat the
place of the city between Moscow and St.Petersburg is extremely economically
profitable. Tver automatically became a large transport junction, crossing
of many tourists routes and, tours. On the other hand closeness to the
capitals creates considerable complications, since both of these megalopolis'
draw human, financial and economic potential of Tver.
 Our
city occupies the territory more than 146 square kilometres. It is 167
km far from Moscow and 485 km far from St.Petersburg. It is located at
the confluence of the rivers Volga, Tvertza and Tmaka. It is connected
with Moscow by three transport main lines: railways, highways and waterways.
In Migalovo region there is one of the largest military aerodromes. For
some years the plans on its widening and turning into a large transport
aerodrome are being worked out. If it takes place Tver will be one of the
biggest transport airport in Russia.
Our
city occupies the territory more than 146 square kilometres. It is 167
km far from Moscow and 485 km far from St.Petersburg. It is located at
the confluence of the rivers Volga, Tvertza and Tmaka. It is connected
with Moscow by three transport main lines: railways, highways and waterways.
In Migalovo region there is one of the largest military aerodromes. For
some years the plans on its widening and turning into a large transport
aerodrome are being worked out. If it takes place Tver will be one of the
biggest transport airport in Russia.